Scientists call for urgent control measures to protect coral reefs from fast-moving, destructive invasion
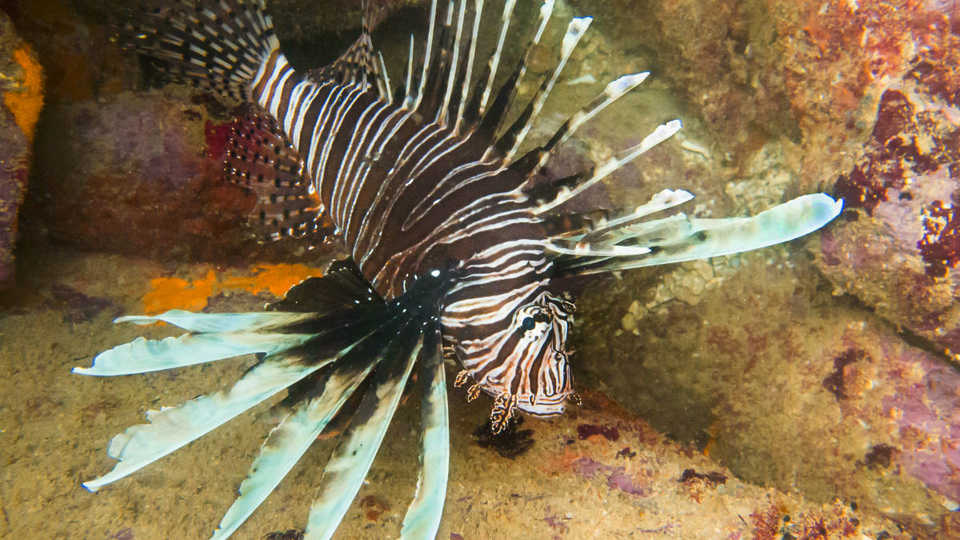
SAN FRANCISCO (April 22, 2015) —A single fish caught with a hand spear off the Brazilian coast is making big waves across the entire southwestern Atlantic. In May 2014, a group of recreational divers spotted an adult lionfish—the voracious invader Pterois volitans—in the rocky reefs of southeastern Brazil. A group of researchers, including scientists from the California Academy of Sciences, used genetic analysis to link the lionfish to the infamous Caribbean population of invaders. In light of a separate study detailing the lionfish penchant for eating critically endangered Caribbean reef fish, news of lionfish in Brazilian waters raises alarm for Atlantic reefs and the region’s already-threatened marine life. The discovery is published this week in PLOS ONE.
“For the past 20 years, invasive lionfishes have been restricted to the Caribbean,” says Luiz Rocha, PhD, Academy curator of ichthyology. “This new record shows us that lionfishes are capable of reaching far into other areas of the Atlantic, and other countries should be on guard, preparing for them to arrive.”
‘A powerful enemy’
Lionfishes are prolific breeders made famous for threatening reef ecosystems outside their native Indo-Pacific distribution. Though the exact cause of their initial Atlantic invasion is unknown, experts believe aquarium dumping in the mid-1990’s is at least partly to blame. With flamboyant fins and vibrant, multi-colored stripes, P. volitans lionfish are popular additions to home aquariums that occasionally end up in nearby waterways.
Once free to breed in open waters, lionfish populations can explode within a short timeframe. Some researchers estimate that one female lionfish can spawn more than two million eggs per year. The researchers say the P. volitans individual found in Brazil probably reached those water via natural long-distance larval dispersal.
“Invasive lionfishes are a powerful enemy to native reef species—many of which are already threatened by habitat destruction and pollution,” says Rocha. “Without natural predators, lionfishes are ‘top dogs’ on the reef. They can easily pick off small, naive reef fish, and do so with gigantic appetite.”
Case studies from the lionfish-ridden Caribbean hint at what is in store for the southwestern Atlantic. Rocha, along with a team of scientists from the Academy and the Smithsonian Institution, recently zeroed in on Belize’s inner barrier reef to study the impact of invasive lionfish on vulnerable Caribbean coral reef ecosystems. The stomach contents of area lionfish—analyzed in the Academy’s Center for Comparative Genomics (CCG)—reveal just how quickly these invaders can devastate native reef populations.
Belize’s critically endagered social wrasse—Halichoeres socialis—made up nearly half of the lionfish diet at the inner barrier reef.
“We found 15 social wrasses in a single lionfish stomach,” adds Claudia Rocha, a molecular biologist at the Academy’s CCG and co-author of the study. “We expected to see several, but the actual number was surpring.”
The researchers concluded that many reef fishes share biological traits—including small size, schooling, and hovering behavior—that make them a target for invasive lionfishes. The combination of lionfish predation, limited range, and ongoing habitat destruction makes the social wrasse the most threatened coral reef fish in the world. Brazilian reef fish with small ranges and analogous traits face similar risks in the face of new lionfish invasions.
Dire consequences in Brazil
Compared to the Caribbean invasion, a lionfish population explosion in Brazilian waters may bring even more severe consequences. Brazilian reefs have relatively lower species diversity but a high number of fish found nowhere else on Earth, many of which have small ranges. The country lacks any formal monitoring programs aimed at early detection of invasive marine species, and is notorious for its struggles with fisheries management.
In December 2014, the Brazilian Minister of the Environment released new national “red lists” identifying 3,286 species of plants and animals threatened with extinction—83 of which are aquatic animals commercially exploited by fisheries. There are no bag or size limits for any species of fish, and commercial fishing interests continue to hamstring efforts to enact new fisheries management plans. As regional ocean health declines in the absence of regulations, fragile reef ecosystems are especially vulnerable to new threats.
“Brazilian fishes are being hit from all sides,” says Rocha. “Overfishing and habitat degradation are pervasive, and not even the most basic fisheries data are being collected. The best—and easiest—way to control an invasion is by trying to slow it down at the start.”
Rocha points out that recreational divers were the first to spot the P. volitans individual in Brazil, and alert local authorities. “It is important,” he says, “that Brazilian recreational divers keep their eyes out for lionfish and report sightings immediately.”
Fish fry
Brazil can take cues from lionfish control efforts in the Caribbean, especially since the P. volitans individual found in Brazil is genetically linked to those invasive populations. In addition to government-enforced marine conservation efforts, Rocha suggests empowering local communities to hunt and cook lionfish.
“Once you get past its poisonous spines, lionfish meat is delicious,” says Rocha. “It’s a delicate white fish that folks in Florida and the Caribbean are learning to safely prepare and sell.”
From lionfish derbies to “catch of the day” specials at local restaurants and supermarkets, coastal communties can help fight the lionfish invasions that devastate nearby marine environments. Lionfish can be the last straw for struggling reef ecosystems and critically endangered marine life, and every individual caught makes a difference.
Visitors to the Academy’s Steinhart Aquarium in Golden Gate Park can see lionfish up-close, and learn more about scientific efforts to track, study, and curb global invasions.
The Institute for Biodiversity Science and Sustainability at the California Academy of Sciences is at the forefront of efforts to understand two of the most important topics of our time: the nature and future of life on Earth. Based in San Francisco, the institute is home to more than 60 research scientists and aquarium biologists, as well as 45.6 million scientific specimens from around the world—nearly 40,000 of which are alive and on display in the Academy's Steinhart Aquarium. The institute also leverages the expertise and efforts of more than 100 international Research and Field Associates and 300 distinguished Fellows. Through expeditions around the globe, captive breeding programs, and investigations in the lab, the institute's scientists strive to understand the evolution and interconnectedness of life. Through these same efforts, as well as through partnerships, community outreach, and public engagement initiatives, the institute aims to guide critical conservation decisions and address the challenge of sustainability. Visit www.calacademy.org for more information.
Press Contacts
If you are a journalist and would like to receive Academy press releases please contact press@calacademy.org.
Digital Assets
Hi-res and low-res image downloads are available for editorial use. Contact us at press@calacademy.org to request access.